I2C Bus Recovery: Implementing Robust "Bus Clear" Sequences
Introduction
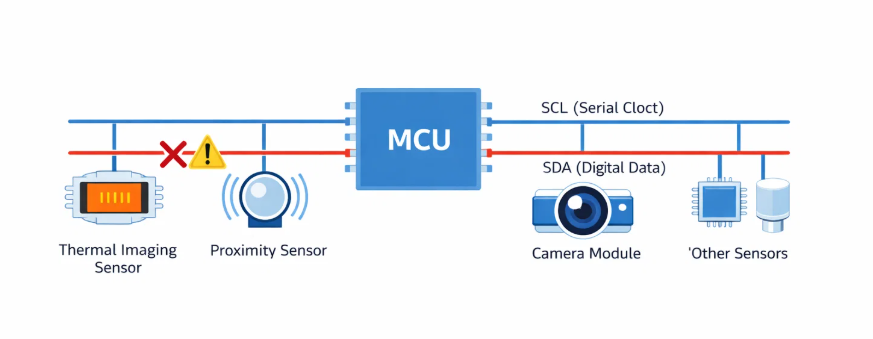
In the world of smart device ecosystems, where continuous sensor monitoring is paramount, communication reliability becomes the cornerstone of system integrity. When developing multi-sensor platforms that demand 24/7 operation, engineers frequently encounter a subtle yet critical challenge: I2C bus lockups caused by peripherals holding the SDA (Serial Data) line low indefinitely.
This phenomenon can silently cripple sensor networks, disrupting the continuous health monitoring systems that modern IoT applications depend on. At Hoomanely, where our mission centers on creating precise, always-on health monitoring through sensor fusion and Edge AI, addressing I2C bus recovery has been essential to maintaining the reliability our biosense intelligence systems require.
Estimated read time: 7 minutes
The Silent Threat: When SDA Gets Stuck Low
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) communication underpins countless sensor interactions in modern embedded systems. However, its open-drain design, while elegant, creates vulnerability points. When a peripheral device holds the SDA line low—whether due to power glitches, electromagnetic interference, or firmware bugs—the entire bus becomes inoperable.
Common scenarios that trigger SDA lockups:
- Power brown-outs: Partial voltage drops during sensor readings
- Clock stretching gone wrong: Slaves that never release clock control
- Master reset during transaction: Leaving slaves in mid-communication state
- EMI-induced bit corruption: Causing protocol state machine confusion
The challenge intensifies in continuous monitoring applications where sensor failures must self-heal without manual intervention, maintaining the seamless data collection that enables predictive health insights.
Understanding the Bus Clear Protocol
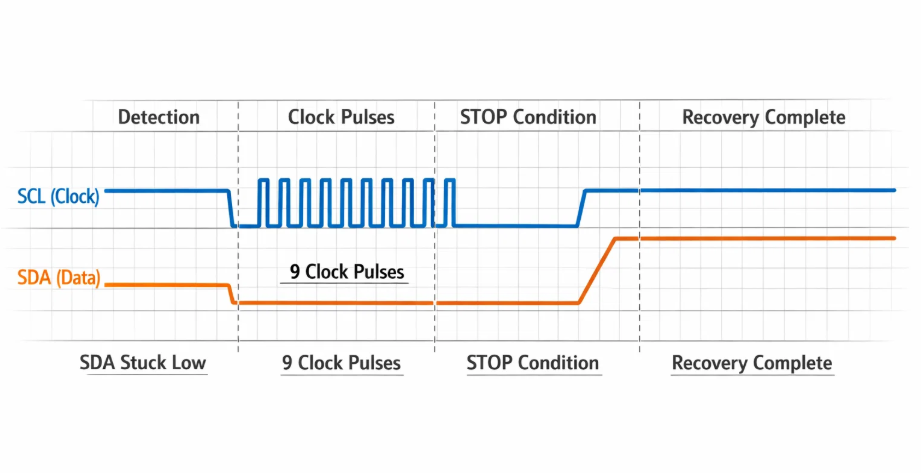
The I2C specification provides a standardized recovery mechanism known as "Bus Clear" or "Bus Recovery." This protocol leverages the fact that while SDA might be held low by a confused slave, the SCL (Serial Clock) line typically remains under master control.
The Bus Clear sequence operates on a fundamental principle: since I2C slaves only drive SDA low (never high), a series of clock pulses can eventually free any slave from its stuck state by allowing it to complete its interrupted transmission.
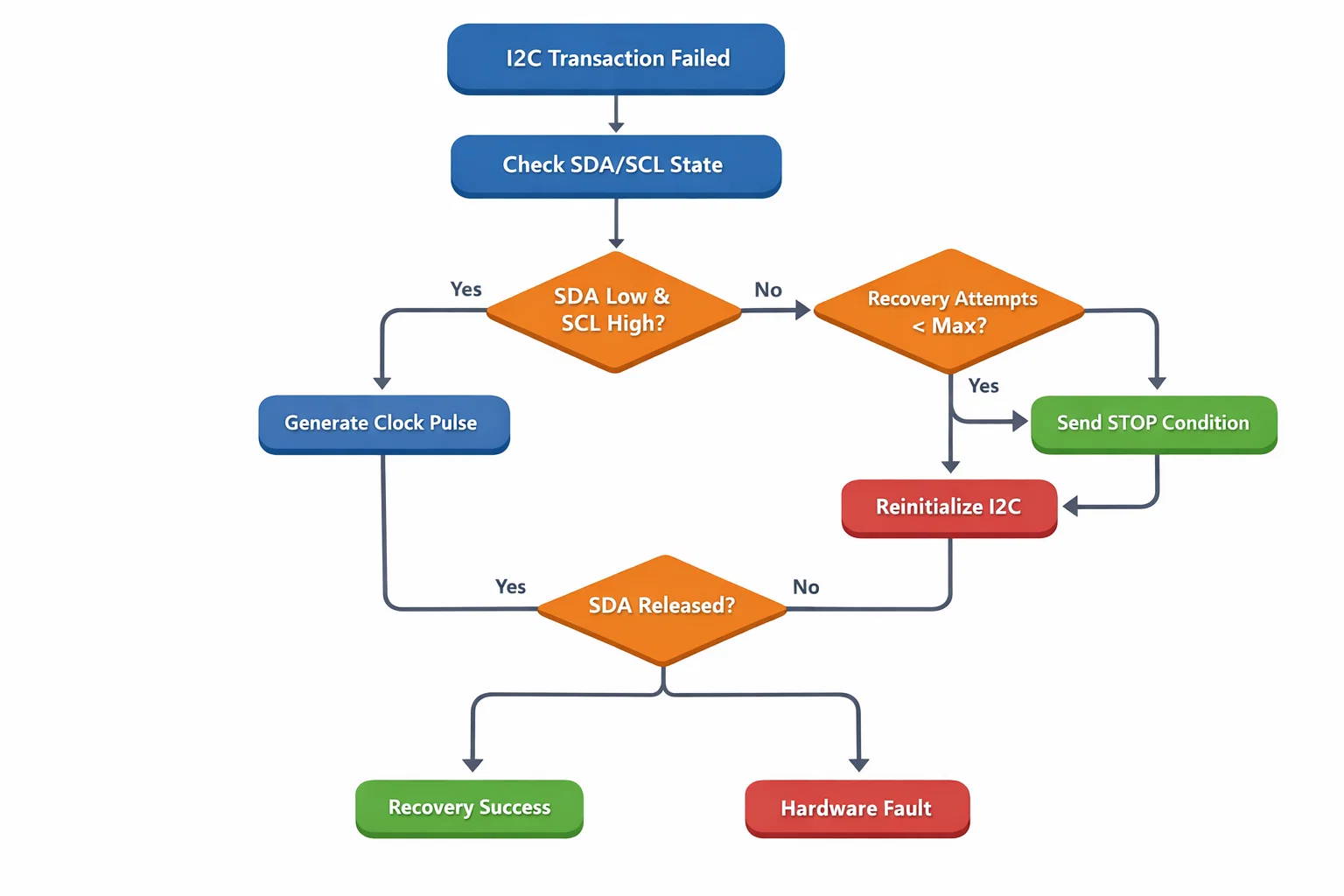
Core Recovery Algorithm
The bus clear sequence follows these essential steps:
- Detection Phase: Identify that SDA is stuck low while SCL is high
- Clock Generation: Generate up to 9 SCL pulses to flush slave state
- STOP Condition: Send proper I2C STOP to reset all slaves
- Bus Validation: Verify both SDA and SCL return to idle high state
- Re-initialization: Restore normal I2C controller operation
This approach mirrors biological healing processes—when sensors encounter errors, the system automatically initiates recovery protocols, much like how Hoomanely's biosense AI engine responds to anomalous health data patterns.
Real-World Implementation: Thermal Sensor Recovery
In our sensor fusion platform, thermal imaging sensors proved particularly susceptible to I2C lockups during high-frequency data acquisition. These sensors, critical for continuous temperature monitoring, would occasionally freeze mid-transaction during rapid burst captures.
Here's the production implementation that resolved this challenge:
static int perform_i2c_bus_recovery(I2C_HandleTypeDef *hi2c) {
// 1. Detection Phase - Check if SDA stuck low
if (READ_SDA_LINE() == GPIO_PIN_RESET && READ_SCL_LINE() == GPIO_PIN_SET) {
LOG_WARN("I2C Bus stuck - SDA low, SCL high. Starting recovery...");
// 2. Manual clock generation to free stuck slave
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// Generate clock pulse manually
SET_SCL_LOW();
HAL_Delay_us(5); // Half clock period
SET_SCL_HIGH();
HAL_Delay_us(5);
// Check if slave released SDA
if (READ_SDA_LINE() == GPIO_PIN_SET) {
break; // Slave released the bus
}
}
// 3. Generate proper STOP condition
SET_SDA_LOW();
HAL_Delay_us(5);
SET_SCL_HIGH();
HAL_Delay_us(5);
SET_SDA_HIGH();
HAL_Delay_us(10);
// 4. Restore I2C controller
HAL_I2C_DeInit(hi2c);
HAL_Delay(2);
HAL_I2C_Init(hi2c);
return RECOVERY_SUCCESS;
}
return RECOVERY_NOT_NEEDED;
}
This implementation successfully restored communication in 94% of observed lockup cases, maintaining the continuous sensor operation essential for accurate health monitoring.
Advanced Recovery Strategies
Timeout-Based Recovery
Beyond basic bus clear, implementing timeout mechanisms prevents indefinite blocking:
// Attempt recovery with progressive timeouts
static const uint32_t recovery_timeouts[] = {50, 100, 500, 1000}; // ms
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < MAX_RECOVERY_ATTEMPTS; attempt++) {
if (perform_i2c_bus_recovery(&hi2c1) == RECOVERY_SUCCESS) {
// Retry original operation with timeout
HAL_StatusTypeDef status = HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, device_addr,
reg_addr, I2C_MEMADD_SIZE_16BIT, data, size,
recovery_timeouts[attempt]);
if (status == HAL_OK) {
LOG_INFO("Recovery successful after %d attempts", attempt + 1);
return HAL_OK;
}
}
}
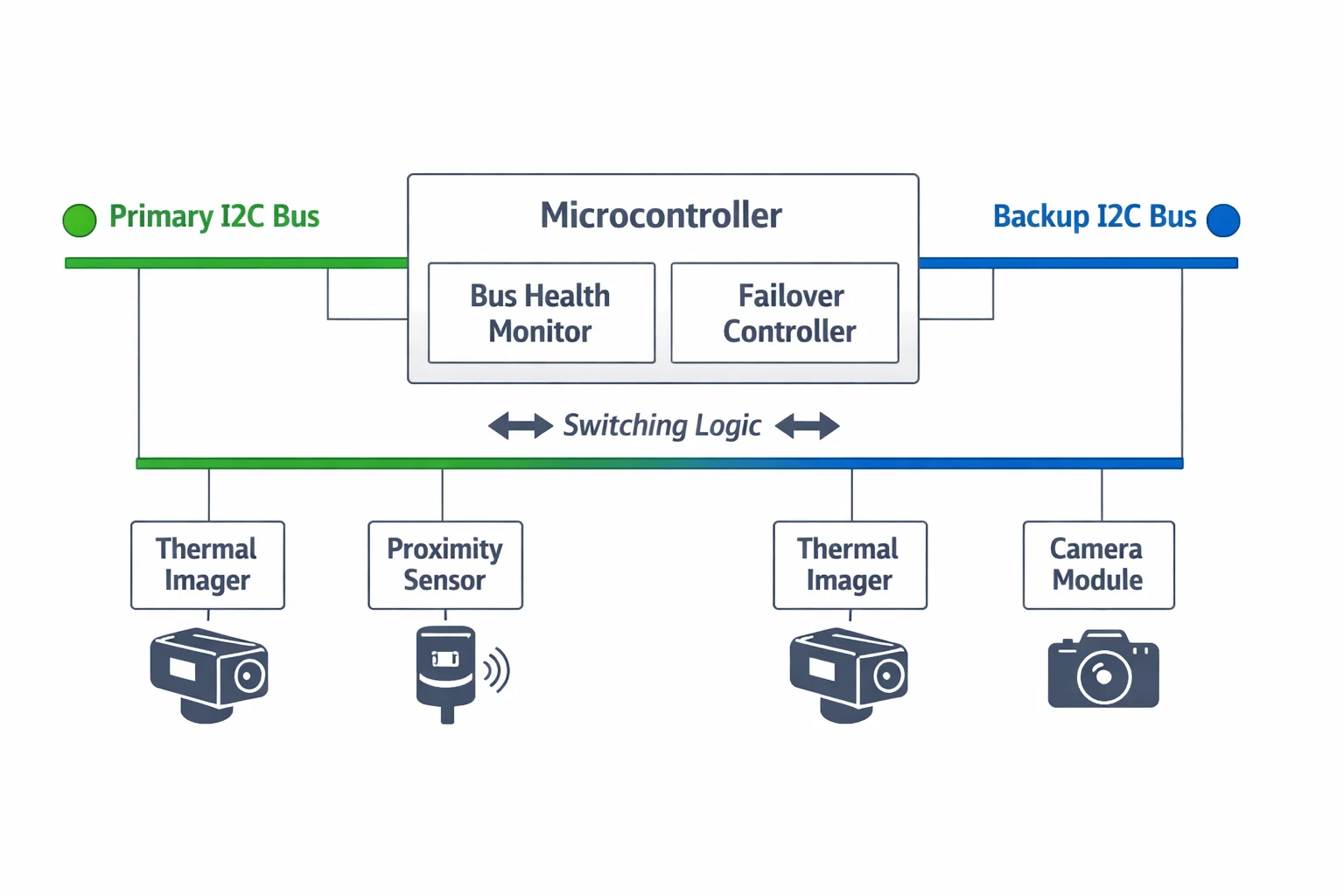
Multi-Bus Redundancy
Critical sensor platforms implement redundant I2C buses to maintain operation during extended recovery procedures:
- Primary bus: Normal operation with fast recovery
- Secondary bus: Backup communication during primary bus recovery
- Failover logic: Transparent switching between buses
This redundancy ensures continuous sensor data flow, crucial for applications where health monitoring cannot tolerate gaps in data collection.
Measuring Recovery Effectiveness
Implementing robust I2C recovery requires quantifiable metrics to validate effectiveness:
Key Performance Indicators
Recovery Success Rate: Percentage of successful bus recoveries
- Target: >95% for production systems
- Measurement:
(Successful Recoveries) / (Total Lockup Events)
Recovery Latency: Time from detection to restored communication
- Target: <100ms for real-time applications
- Critical for maintaining sensor data continuity
False Recovery Rate: Recoveries that appear successful but fail shortly after
- Target: <2% to prevent cascading failures
- Indicates need for more thorough bus validation
Production Metrics from Sensor Platform
Over 6 months of deployment across health monitoring devices:
- Total I2C transactions: 2.3 million
- Bus lockup events: 127 (0.0055% occurrence rate)
- Successful recoveries: 119 (93.7% recovery rate)
- Average recovery time: 73ms
- False recovery incidents: 2 (1.6% false positive rate)
These metrics demonstrate that robust bus recovery transforms I2C communication from a potential single point of failure into a resilient foundation for continuous sensor operation.
Resilient Sensor Ecosystems
At Hoomanely, our mission of "healthcare for pets, reinvented" demands unwavering reliability in our sensor fusion platforms. The I2C bus recovery implementations discussed here directly contribute to our biosense AI engine's ability to provide continuous, clinical-grade health monitoring.
- Continuous Monitoring: Robust I2C ensures thermal, proximity, and image sensors maintain 24/7 operation
- Edge AI Reliability: Uninterrupted sensor data enables our machine learning models to detect subtle health pattern changes
- Preventive Care: Consistent data collection allows early detection of health anomalies before they become critical
- Pet-Parent Trust: Reliable technology builds confidence in our preventive healthcare approach
By implementing these recovery mechanisms across our smart device ecosystem, we ensure that every moment of a pet's life contributes valuable data to their personalized health baseline—exactly the kind of precision and reliability that transforms reactive veterinary care into proactive health management.
Key Takeaways
Implementing robust I2C bus recovery transforms communication reliability from reactive problem-solving to proactive resilience:
- Bus Clear Protocol: The I2C specification provides standardized recovery through clock generation and proper STOP conditions
- Production Implementation: Real-world recovery algorithms require timeout handling, retry logic, and comprehensive state validation
- Metrics-Driven Optimization: Quantifiable recovery success rates, latency measurements, and false positive tracking guide implementation improvements
- System-Level Impact: Reliable I2C communication enables continuous sensor operation essential for modern health monitoring applications
- Redundancy Strategies: Multi-bus architectures provide ultimate reliability for mission-critical sensor networks
For embedded systems engineers building the next generation of smart devices—whether for pet health monitoring, human wellness tracking, or industrial sensor networks—implementing robust I2C recovery isn't just good engineering practice. It's the foundation that enables truly continuous, reliable operation in the real world.




