Shadow RAG: Observation Layer

If you’ve ever shipped a RAG system into production, you already know the uncomfortable truth: these systems don’t fail dramatically. They fail quietly. No alarms. No error stacks. No catastrophic crashes. One day the answers simply aren’t as sharp as they used to be. The assistant feels slightly off. Troubleshooting flows start requiring more follow-ups. Behavioral explanations lose nuance. Health guidance becomes oddly verbose.
It’s the kind of slow drift that only mature engineers notice. Something changed, but you can’t tell what. And even if you wanted to track it down, there’s usually no single culprit—retrieval tweaks, index updates, new embedding models, prompt revisions, or a fresh LLM can all produce subtle, unpredictable side effects.
Most organizations respond the way anyone does under uncertainty:
they poke the system, adjust something, deploy, and hope.
But hope-based iteration doesn’t scale.
Not when the assistant supports real customers.
Not when accuracy matters.
Not when tone influences trust.
Not when retrieval is the backbone of correctness.
Shadow RAG exists to solve this problem. It gives teams a way to experiment safely, evaluate deeply, and evolve RAG systems with the same discipline we expect from backend architecture or model training pipelines. Instead of deploying retrieval or generation changes into the live path, you mirror a subset of real production traffic into alternative pipelines. These shadow pipelines process the same queries but never influence the user experience. Their outputs are captured, diffed, and compared—giving you a living, breathing evaluation dataset straight from the real world.
For teams building systems like Hoomanely’s EverWiz assistant—with knowledge spanning pet nutrition, behavior interpretation, device troubleshooting, firmware notes, and sensor diagnostics—Shadow RAG becomes a non-negotiable safety rail. It ensures that new strategies don’t accidentally break the flows that matter most, and that improvements are measured, not imagined.
Let’s unpack how Shadow RAG works, why it matters, and what it reveals about RAG systems that traditional evaluation pipelines miss entirely.
Why RAG Systems Drift
RAG systems evolve continuously, often in ways no one intentionally planned. Even the smallest change has downstream effects:
Retrieval drift
A new embedding model shifts similarity scores. Tokens cluster differently. Dense retrieval starts surfacing passages that look good semantically but ignore tiny lexical clues that matter—IDs, error codes, sensor names.
Chunking drift
Two lines of code change chunk size from 512 to 384 tokens. Retrieval becomes sharper for short queries but blind to long-form reasoning. The assistant feels “less deep,” even if correctness remains high.
Index drift
Reindexing can:
- reorder document sections
- change analyzer behavior
- remove legacy content
- collapse duplicates with different embeddings
- alter sparse/dense indexing mix
Even if retrieval still returns relevant passages, the nuance may disappear.
Model drift
LLMs are notoriously sensitive to context:
- a new version of Llama or Claude may rewrite answers more politely
- or more aggressively
- or more vaguely
- or more confidently
These changes often go unnoticed in offline evaluations.
Prompt drift
Prompts expand, shorten, reorder, or gain system-level rules. A tiny phrasing difference pushes the LLM to reinterpret the sequence of thought, or to handle uncertainty differently.
Operational drift
Retrieval or generation changes influence:
- latency distribution
- cost per request
- token usage
- likelihood of timeouts
- fallback paths
These are invisible unless intentionally monitored.
The reality is simple:
A RAG system is a living ecosystem. Without continuous observation, it drifts.
Shadow RAG doesn’t fight this drift—
it exposes it.
What Shadow RAG Actually Is
Shadow RAG is not an A/B test. It’s not a deployment strategy. It’s not a traffic-splitting mechanism. It is a parallel evaluation architecture.
Here’s the shortest possible explanation:
Production handles the user.
Shadow pipelines handle curiosity.
A shadow pipeline receives a mirrored copy of the user query, processes it independently, and logs every detail of its retrieval and generation path. The user never sees the shadow output. The product remains untouched. But the engineering team now has a real dataset of how new strategies behave across thousands of authentic production queries.
This is the difference between “I think dense retrieval is better” and “dense retrieval outperformed lexical retrieval across 8 out of 12 query clusters, but underperformed significantly in troubleshooting.”
Shadow RAG turns assumptions into evidence.
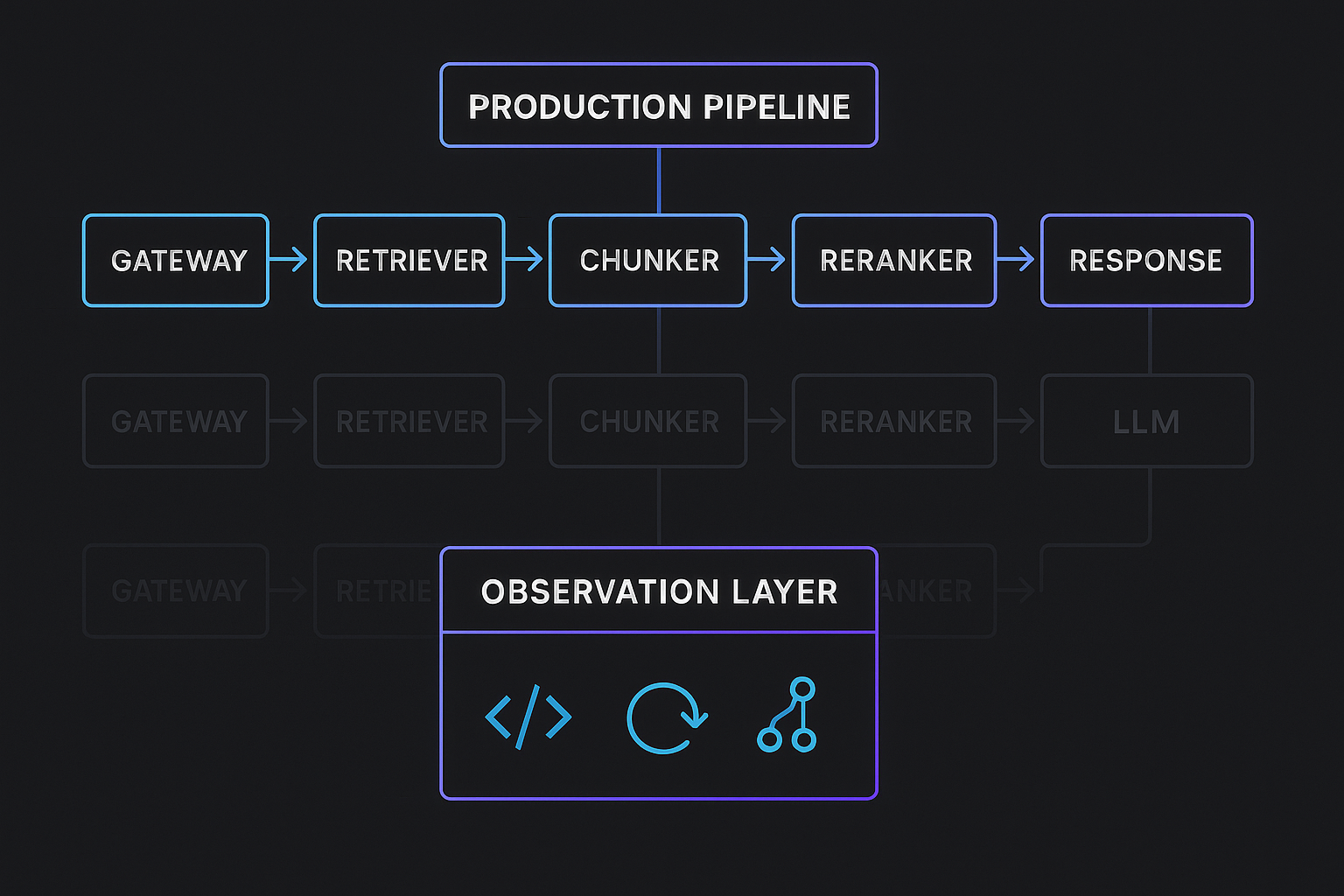
Why Offline Evaluation Isn’t Enough
Most RAG teams create a “test set” of maybe 200–500 queries. It feels comprehensive. It contains a mix of:
- expected user questions
- known corner cases
- tricky phrasing
- troubleshooting flows
- high-impact health/behavior questions
- long-form reasoning tasks
But these hand-crafted datasets—even if lovingly curated—don’t capture the distribution of real user queries.
Real-world traffic includes:
- incomplete sentences
- multi-lingual fragments
- “explain this like I’m five” phrasing
- emotionally charged requests
- questions containing telemetry values
- device-specific jargon
- syntactically broken inputs
- queries with contradictory or partial context
- recurring issues rephrased subtly each time
No curated dataset can simulate this.
Shadow RAG evaluates against actual traffic.
This matters especially for platforms like Hoomanely, where queries can swing wildly between:
- “My device is blinking red.”
- “How many calories for a senior labrador?”
- “Why did my pet do X today?”
- “Show me yesterday’s sensor data spikes.”
- “What does this firmware error mean?”
Different pipelines behave differently across these domains—and Shadow RAG brings those differences into the light.
A Conversational Deep Dive Into the Architecture
Let’s walk through the architecture the same way a senior engineer would explain it on a whiteboard—not as a tutorial, but as a conceptual flow.
1. Gateway-Level Mirroring
The gateway receives the request. It executes production logic immediately. Then, based on sampling rules, it sends a clone of the request into a background task running shadow pipelines.
Sampling can be:
- percentage-based
- deterministic
- cluster-based (e.g., “mirror all troubleshooting queries”)
- user-tier based
Shadow RAG’s gateway-level separation ensures that:
- The main request path is unaffected
- Shadow pipelines can be slow
- Shadow pipelines can fail silently
- Shadow pipelines can run heavier retrieval or generation logic safely
Think of it as “Tap into the stream, but don’t disturb it.”
Minimal code snippet to illustrate the feeling:
if shadow_router.mirror(request):
asyncio.create_task(shadow_runner.run(request))
2. Pipeline Registry
Each pipeline represents one hypothesis.
Examples:
- “Smaller chunks might improve reasoning.”
- “Dense retriever might catch more behavior context.”
- “Hybrid retriever might improve troubleshooting.”
- “New Bedrock model might reduce hallucination.”
- “Rewritten prompt might give cleaner summaries.”
Pipelines are versioned and immutable:
PIPELINE_REGISTRY = {
"prod": ProdPipeline(),
"dense_v1": DenseRetrieverPipeline(),
"chunk_384_v2": ChunkingExperiment(),
"llama3_11B_prompt_v4": PromptExperiment(),
}
This keeps the system honest.
No silent mutations.
3. Retrieval Comparison
This is where the magic happens.
Shadow RAG doesn’t just capture “which documents were retrieved.”
It captures the shape of retrieval:
- How diverse?
- How dense or sparse?
- How overlapping with production?
- How stable across similar queries?
- How sensitive to wording?
- How well does it capture rare or long-tail documents?
This matters because retrieval quality determines everything else.
If production retrieves:
- “Temperature drift diagnostic doc”
- “Calib pattern v1.8”
- “Thermal anomaly quick-ref”
…but the shadow pipeline retrieves:
- “Thermal failure troubleshooting”
- “Pet activity during warm cycles”
- “How to clean device interior”
Then you already know the downstream differences will be massive.

4. Generation Divergence
Even with identical retrieval, LLMs behave differently:
- more verbose
- more cautious
- more speculative
- more empathetic
- more formal
- more assertive
Shadow RAG captures these subtle changes through semantic diffs.
An example of what engineers often discover:
- A model producing shorter answers may actually be more correct
- A model producing longer answers may be inflating reasoning
- A model with better coherence may hallucinate more convincingly
- A new prompt may stabilize tone but reduce factual directness
Shadow RAG reveals the character of the model.
A tiny semantic diff snippet
score = llm_evaluator.semantic_diff(prod_text, shadow_text)
Not rocket science.
But powerful when repeated across 10,000 queries.
5. Operational Behavior
Shadow RAG also surfaces operational patterns:
- latency drift
- token drift
- cost differences
- cold-start anomalies
- caching impacts
- timeout trends
- error rate differences
For example:
- A chunking strategy that improves retrieval quality may spike p95 latency.
- A heavier reranker may barely affect latency for small queries but explode on large ones.
- A new embedding model may stress OpenSearch more than expected.
- A newer LLM may be “cheaper” in tokens but slower in inference.
These are business decisions as much as technical ones.
Shadow RAG reveals operational trade-offs early.
In Hoomanely’s ecosystem, Shadow RAG plays a crucial role in ensuring:
- health guidance remains grounded
- behavioral explanations remain contextual
- troubleshooting remains literal and precise
- firmware flows remain stable
- sensor diagnostics remain interpretable
Without Shadow RAG, retrieval improvements for nutrition might break troubleshooting.
Or a new model that helps behavioral insight might hallucinate sensor states.
Shadow RAG ensures the entire AI layer evolves safely across domains.
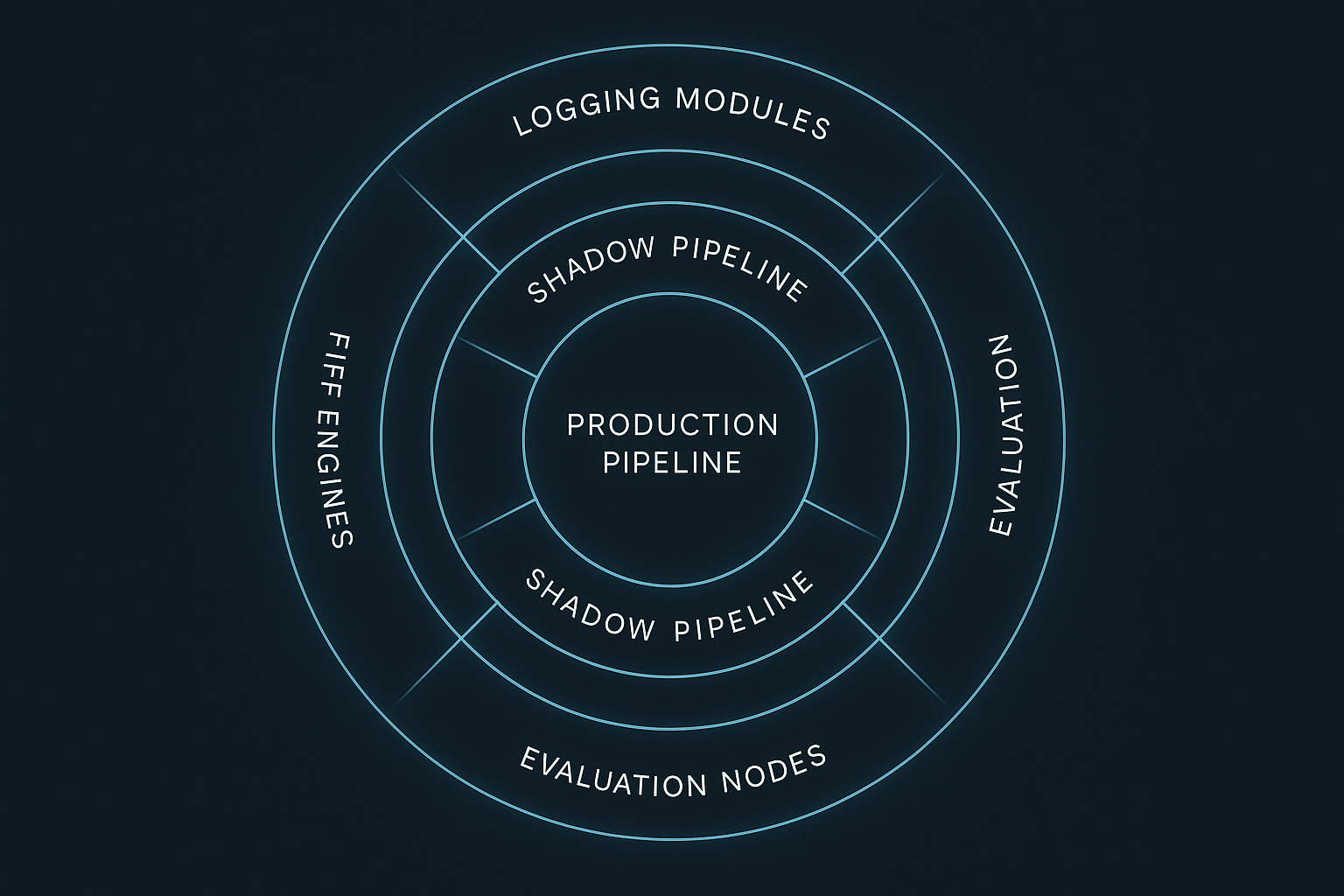
A Realistic Mental Model of Shadow RAG’s Value
Think of it like this:
- Production is your system’s memory.
- Shadow pipelines are your system’s imagination.
- Shadow logs are your system’s journal.
- Semantic diffs are your system’s X-rays.
- Retrieval comparison is your system’s microscope.
- Operational signals are your system’s vital signs.
- Your review tooling is your system’s language for understanding itself.
Shadow RAG gives the system the ability to observe itself—without risk.
That’s the real value.
What Teams Typically Discover Through Shadow RAG
Some of the patterns repeatedly observed across companies:
1. Chunk size matters more than anyone expects.
384 tokens might outperform 512 in nine categories but fail spectacularly in long-context flows.
2. Dense retrievers are fantastic… until they’re not.
They miss rare documents at the worst possible moments.
3. Rerankers are double-edged swords.
Precision improves, but latency spikes in unpredictable ways.
4. Embedding upgrades reorganize semantic neighborhoods.
Entire clusters of docs shift to new similarity groups.
5. LLM upgrades compress reasoning.
This often cuts hallucinations but also reduces nuance.
6. Prompts influence operational metrics.
A seemingly “cleaner” prompt may increase output tokens by 30%.
7. Index design silently dictates system behavior.
The documents you cluster together matter. The ones you don’t matter even more.
Shadow RAG makes these patterns not just visible—but obvious.
Takeaways
Shadow RAG is not one more tool in your toolbox.
It is the safety net underneath your entire RAG evolution strategy.
Why it matters:
- Real traffic is the only true evaluation dataset
- Retrieval drift is invisible without parallel pipelines
- Generation drift is subtle and psychological
- Operational drift influences cost and reliability
- Shadow RAG turns experimentation from guessing into observing
- It protects production while accelerating innovation
- It aligns backend, ML, and product teams on shared truth
- It ensures that evolution remains trustworthy
Shadow RAG is how organizations ship improvements safely, continuously, and confidently.




